Last updated on September 26th, 2024 at 11:15 am
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment involves a comprehensive approach to manage the disease’s symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow down joint damage. It typically includes medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), lifestyle modifications, exercise, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Early diagnosis and individualized rheumatoid arthritis treatment plans are key to effective management.
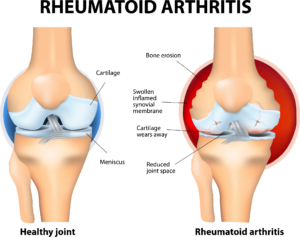
RA is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints and causes inflammation, pain, and joint damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is primarily a result of wear and tear on the joints, RA is characterized by the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking healthy joint tissues. This chronic inflammatory condition often leads to joint deformities, loss of mobility, and decreased quality of life if left untreated.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
While there is no cure for RA, several rheumatoid arthritis treatment options are available to manage its symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals living with RA. These rheumatoid arthritis treatments can be broadly categorised into medications, lifestyle changes, and surgical interventions.
1. Medication
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs are the cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis treatment. They work to suppress the overactive immune system, reduce inflammation, and slow down the progression of joint damage. Common DMARDs include:
- Methotrexate: Often the first-line choice, methotrexate is effective in managing RA symptoms and preventing joint damage.
- Hydroxychloroquine: This medication is particularly useful for mild RA and is sometimes used in combination with other DMARDs.
- Sulfasalazine: Another option for mild to moderate RA, sulfasalazine can help reduce inflammation and joint pain.
- Biologic DMARDs: Biologics are a newer class of medications that target specific molecules in the immune system responsible for inflammation. These medications are often used when conventional DMARDs are ineffective or poorly tolerated. Examples of biologic DMARDs include:
- Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Inhibitors: Medications like adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab are TNF inhibitors that have been successful in treating RA.
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors: Tocilizumab is an example of an IL-6 inhibitor that can be effective in RA treatment.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors: Tofacitinib and baricitinib are JAK inhibitors that work to reduce inflammation in RA patients.
- Corticosteroids: Short-term corticosteroids, such as prednisone, may be necessary during RA flares to rapidly control inflammation and pain. However, long-term use is typically avoided due to potential side effects.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help maintain joint function, reduce stiffness, and improve overall well-being. Low-impact exercises like swimming, yoga, and tai chi are often recommended for individuals with RA.
- Diet: While there is no specific RA diet, maintaining a healthy and balanced diet can support overall health. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish and anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may benefit.
- Rest: Adequate rest and sleep are essential for managing RA symptoms. Fatigue is a common symptom of RA, and getting enough rest can help reduce its impact.
- Stress Management: High levels of stress can exacerbate RA symptoms. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
3. Surgical Interventions
- Joint Surgery: In cases where joint damage is severe and pain is not adequately controlled with medications, surgical options may be considered. Joint surgeries can range from minimally invasive arthroscopy to full joint replacements (e.g., knee or hip replacement).
- Synovectomy: This procedure involves the removal of the inflamed synovial tissue that lines the joint. It is usually performed to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Tendon Repair: RA can cause damage to tendons around the affected joints. To restore function, surgical repair may be necessary.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
4. Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Some individuals with RA find relief through complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and dietary supplements. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any of these rheumatoid arthritis treatments, as their effectiveness can vary, and some may interact with RA medications.
Conclusion:
The journey of rheumatoid arthritis treatment has been marked by remarkable progress in recent years. From traditional DMARDs to innovative biologics and emerging therapies, there is newfound hope for individuals living with RA. Early diagnosis, personalized rheumatoid arthritis treatment plans, and a holistic approach to care are shaping the future of RA management.
While challenges persist, the ongoing commitment to research and patient-centred care offers optimism for a brighter and more comfortable future for those affected by this autoimmune condition. As the medical community continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can look forward to a better quality of life and improved treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis on the horizon.
Difference Between Patent And Generic Medicine
Patent medicines are brand-name drugs developed by pharmaceutical companies and protected by patents, allowing them exclusive rights to sell the drug for a specific period. They are usually more expensive due to research and development costs.
In contrast, generic medicines are identical copies of patent medicines with the same active ingredients, quality, and efficacy, but they are produced and sold after the patent expires. Generics are typically more affordable since manufacturers do not bear the initial research expenses.
FAQs on Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Q:1 What is rheumatoid arthritis treatment?
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow joint damage, and reduce inflammation. It often involves medications like DMARDs and biologics, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. Early diagnosis and a personalized approach are crucial for effective management.
Q:2 Can I manage rheumatoid arthritis with over-the-counter pain relievers?
Over-the-counter pain relievers may provide temporary relief, but for effective management, consult a healthcare provider for prescription medications like DMARDs or biologics.
Q3: Is surgery the only option if my rheumatoid arthritis worsens?
Surgery is considered when other treatments are ineffective. It’s important to explore various medications and therapies with your rheumatologist before considering surgical intervention.
Related Links:
