Last updated on September 26th, 2024 at 11:15 am
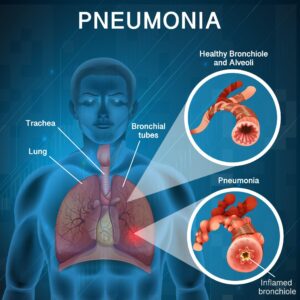
Pneumonia Treatment – When it comes to respiratory infections, pneumonia is a formidable adversary. Characterized by inflammation of the lung tissue, this condition can be mild or severe, but one thing is clear – timely and effective treatment of pneumonia is crucial for a swift recovery. Pneumonia, a common and potentially serious respiratory infection, demands comprehensive and effective treatment to ensure a full recovery.
Pneumonia Treatment
Prompt diagnosis is the cornerstone of successful treatment of pneumonia. As soon as symptoms such as high fever, cough with mucus production, chest pain, and difficulty breathing manifest, seeking medical attention is imperative.
Healthcare professionals employ a combination of physical examinations, chest X-rays, and, in some cases, blood tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the condition.
Pneumonia Treatment Medication
The majority of pneumonia cases are caused by bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae. For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are the primary treatment modality. These medications work to eliminate the invading bacteria, allowing the body’s natural defences to regain control of the infection.
Tailored Antibiotics:
One crucial aspect of the treatment of pneumonia is selecting the appropriate antibiotics. The choice depends on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the suspected or identified bacteria causing the infection. Healthcare providers prescribe antibiotics specific to the type of bacteria present to ensure the highest efficacy and prevent antibiotic resistance.
Patients need to complete the entire prescribed course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps prevent the resurgence of the infection and ensures that all bacteria are eradicated.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
Treatment of Pneumonia Therapies
Beyond antibiotics, various supportive therapies play pivotal roles:
Oxygen Therapy: In severe cases of pneumonia, where oxygen levels in the blood are significantly reduced, supplemental oxygen may be necessary. Oxygen therapy ensures the body receives sufficient oxygen to function properly, allowing the patient to recover more effectively.
Intravenous (IV) Fluids: Dehydration is a common concern during pneumonia due to fever, reduced fluid intake, and increased respiratory effort. Intravenous fluids can help maintain hydration levels, support the immune system, and facilitate the body’s recovery.
Chest Physiotherapy: This technique involves specialized manoeuvres to help clear mucus from the airways, making breathing easier. Chest physiotherapy is particularly beneficial for patients with excessive mucus production or difficulty expelling it.
Pneumonia – Hospitalization in Severe Cases
While many cases of pneumonia can be managed on an outpatient basis, severe pneumonia or complications may necessitate hospitalization. Hospital care offers closer monitoring, more intensive treatments, and access to respiratory support, including mechanical ventilation if needed.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
Personalized Care Plans for Pneumonia
Every patient’s response to the treatment of pneumonia varies, necessitating individualized care plans. Healthcare providers consider factors like:
- Age
- Overall health
- Underlying conditions when tailoring treatment approaches.
Pneumonia Treatment at Home
Follow Medication Instructions: It’s crucial to adhere to your prescribed medication regimen. Finish the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before it’s completed. This helps ensure that all bacteria are eradicated, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Manage Symptoms: Pneumonia can cause uncomfortable symptoms such as fever, cough, and chest pain. Over-the-counter medications and pain relievers can help alleviate these discomforts. Constantly, consult with your healthcare provider before accepting any new medications.
Isolation and Rest: During your recovery, it’s advisable to isolate yourself to prevent spreading the infection to others. Rest is paramount – it allows your body to heal and regenerate.
Post-Treatment Care and Prevention
Once the acute phase of treatment of pneumonia is completed, post-treatment care becomes crucial. This phase includes:
Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor progress, assess lung function, and address any lingering symptoms or concerns.
Reinforcing Preventive Measures: To reduce the risk of pneumonia recurrence, healthcare providers may recommend vaccinations, lifestyle changes (such as smoking cessation), and preventive medications in some cases.
Conclusion:
Pneumonia treatment is a multifaceted endeavour, aiming not only to eliminate the infection but also to support the patient’s overall health and recovery. The timely use of antibiotics, coupled with supportive therapies, can significantly improve outcomes. Additionally, post-treatment care and preventive measures are essential to minimize the risk of future pneumonia episodes.
By seeking medical attention promptly, adhering to treatment plans, and embracing preventive strategies, individuals can overcome pneumonia and regain their respiratory health. Pneumonia may be a formidable foe, but with the right treatment and support, victory is within reach.
FAQs on Pneumonia Treatment
Q.1 What is Pneumonia Treatment?
Pneumonia treatment typically involves antibiotics for bacterial cases, rest, hydration, and supportive therapies like oxygen and chest physiotherapy. It’s crucial to complete the prescribed antibiotic course and consult a healthcare provider for personalized care.
Q2. What is the typical duration of treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics?
The duration of treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection. In most cases, healthcare providers prescribe antibiotics for a period of 5 to 10 days. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medicine is finished. This helps ensure that all bacteria causing the infection are eradicated and reduces the risk of recurrence.
Related Links: