Last updated on December 31st, 2024 at 05:00 pm
Jaundice treatment encompasses a range of medical interventions aimed at addressing the underlying causes of this condition and alleviating its associated symptoms. When it comes to jaundice treatment, the approach depends on the specific diagnosis, severity, and individual patient factors.
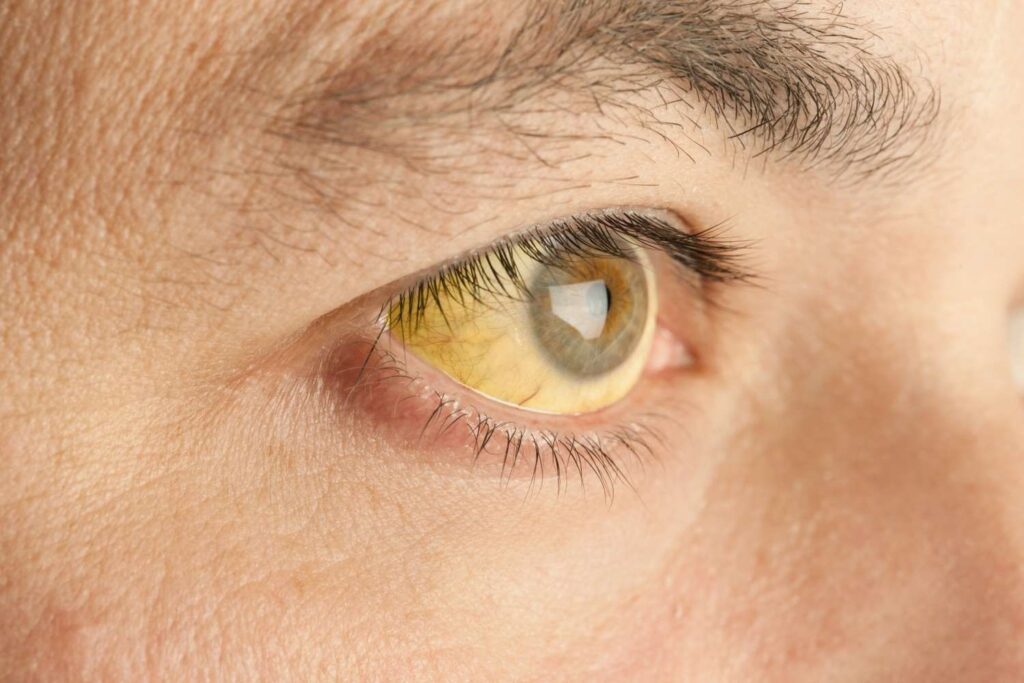
Jaundice, medically known as icterus, is a condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes due to an elevated level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin, a vibrant yellow pigment, emerges as a byproduct of the breakdown of red blood cells.
What is Jaundice?
Jaundice arises when an abundance of bilirubin accumulates in the bloodstream. Jaundice can be caused by various underlying medical conditions, such as liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or bile duct obstruction.
Effective treatment of jaundice depends on identifying and addressing the root cause. Bilirubin, a yellow pigment, is generated as a result of the breakdown of red blood cells. Numerous factors that can contribute to the onset of jaundice are :
1. Liver Dysfunction
The liver plays a crucial role in processing bilirubin and removing it from the body. Any dysfunction in the liver can disrupt this process, leading to jaundice. Common liver conditions include hepatitis, cirrhosis, and alcoholic liver disease.
2. Hemolytic Anemia
In cases where red blood cells break down rapidly, such as in hemolytic anemia, the body may struggle to eliminate bilirubin efficiently. This can result in jaundice.
3. Bile Duct Obstruction
A blockage in the bile ducts can prevent the flow of bile, causing bilirubin to accumulate in the bloodstream. Gallstones and tumours can lead to such obstructions.
Now that we understand the causes let’s delve into the essential aspects of jaundice treatment.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?

Jaundice Treatment
When it comes to treating jaundice, several approaches can help alleviate symptoms and address the underlying causes:
1. Medical Intervention
In cases of severe jaundice or when it is caused by an underlying medical condition, medical intervention is essential. This may involve hospitalization, where doctors can provide treatments such as blood transfusions, medication, or surgery to address the root cause.
Specific medications may be prescribed:
- Antiviral drugs: For hepatitis-related jaundice.
- Corticosteroids: In some autoimmune liver diseases.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid: To dissolve gallstones in cases of gallstone-related jaundice.
Surgery or Procedures: In certain cases, surgical interventions or procedures may be necessary:
- Liver Transplant: When liver disease is advanced and irreversible.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): To remove bile duct obstructions.
- Gallbladder Removal: If gallstones are causing bile duct blockage.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
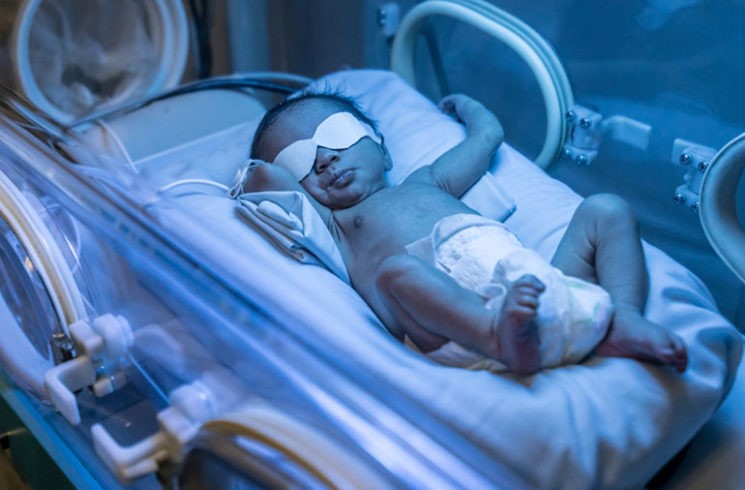
2. Phototherapy
For newborns with jaundice, phototherapy is a common treatment method. Special lights are used to help break down excess bilirubin in the baby’s body. It’s a safe and effective way to manage jaundice in infants.
Treating the Underlying Cause:
The primary focus of jaundice treatment is to address the underlying condition responsible for the elevated bilirubin levels. Common causes of jaundice and their respective treatments include:
- Liver Disease: Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or even a liver transplant in severe cases.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Managing the underlying anaemia with blood transfusions, medications, or spleen removal.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: Surgical intervention or endoscopic procedures to remove obstructions or relieve blockages.
3. Dietary Adjustments
- A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in jaundice treatment, especially for patients with liver conditions. The diet should be low in fat and alcohol and should focus on providing essential nutrients.
- In cases of obstructive jaundice, a low-fat diet can help reduce the workload on the liver and improve digestion.
- Hydration is essential to prevent dehydration and promote overall well-being.
Symptoms for Jaundice
A few of the symptoms of jaundice are discussed below:
- Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes: The most noticeable sign, causes the skin and the whites of the eyes to turn yellow.
- Dark Urine: Urine can appear dark or brownish in colour due to increased bilirubin levels.
- Pale Stool: The stool may become pale or clay-coloured as bilirubin is not properly excreted into the digestive tract.
- Fatigue: Jaundice can lead to tiredness and weakness.
- Itching (Pruritus): Some individuals experience itching, which is often a result of bilirubin accumulation in the skin.
- Abdominal Pain: In cases of underlying liver or gallbladder issues, abdominal discomfort or pain may occur.
- Nausea and Loss of Appetite: Jaundice can lead to feelings of nausea, and individuals may lose their appetite.
It’s important to note that the severity and combination of these symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause of jaundice. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of Jaundice
The diagnosis of jaundice typically involves the following:
- Physical Examination: A physical examination will be conducted to assess the extent of jaundice and check for any underlying causes, such as liver or gallbladder issues.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, including liver function tests and bilirubin levels, are essential for diagnosing jaundice. Elevated bilirubin levels in the blood confirm the presence of jaundice.
- Imaging Studies: In some cases, imaging studies like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans may be performed to visualize the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts to identify any structural abnormalities or blockages.
- Liver Biopsy: In certain situations, a liver biopsy may be recommended to assess the extent of liver damage and help determine the underlying cause, especially if liver disease is suspected.
The combination of these diagnostic methods helps healthcare professionals identify the underlying cause of jaundice and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Early diagnosis is crucial to address the root cause and manage jaundice effectively.
Preventing Jaundice
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of developing jaundice:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly.
- For protection of the liver, limit alcohol consumption.
- Practice safe sex and get vaccinated for hepatitis to reduce the risk of liver infections.
- Be cautious with over-the-counter medications and follow recommended dosages.
Conclusion:
Jaundice is a condition that should not be taken lightly. Understanding its causes and seeking appropriate treatment is essential for a speedy recovery. Whether it’s through medical intervention, phototherapy, or addressing underlying conditions, managing jaundice effectively is possible. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing jaundice in the first place.
Remember, if you suspect you or a loved one may have jaundice, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Timely intervention plays a pivotal role in ensuring a triumphant path towards recovery.
FAQs On Jaundice Treatment
Q.1 What is Jaundice Treatment?
Jaundice treatment refers to the medical interventions and strategies employed to address the underlying causes of jaundice and alleviate its symptoms. Jaundice is a medical condition distinguished by the manifestation of a yellow hue in both the skin and the sclera (the whites of the eyes).
Q.2 What is the primary aim of jaundice treatment?
The jaundice treatment aims to:
- Identify and Address the Underlying Cause
- Symptomatic Relief
- Dietary Adjustments
- Medications
- Surgical Procedures
- Monitoring and Follow-up
Q3. What is the typical duration of jaundice treatment?
The duration of jaundice treatment varies depending on the underlying cause and its severity. In some cases, jaundice may resolve within a few weeks with appropriate treatment, while chronic conditions might require long-term management. For instance, viral hepatitis-related jaundice can improve within a few weeks to months, whereas liver diseases may necessitate ongoing treatment and monitoring.
Related Links: