Last updated on September 26th, 2024 at 11:15 am
Hyperthyroidism treatment involves methods to regulate the overproduction of thyroid hormones. The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, energy production, and body temperature.
When this gland goes into overdrive, producing an excess of thyroid hormones, it can lead to a range of distressing symptoms and potential health complications. Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available to restore balance to the body and alleviate the burdens of hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment
Before delving into hyperthyroidism treatment options, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of hyperthyroidism. This condition, also known as overactive thyroid or thyrotoxicosis, occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
These hormones play a central role in regulating the metabolism of the body. When their levels are too high, it sets off a chain reaction that can affect nearly every system in the body.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
Symptom of Hyperthyroidism
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune disorder called Graves’ disease, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, stimulating it to produce more hormones. Other potential causes include thyroid nodules or goitres, excessive iodine intake, and certain medications.
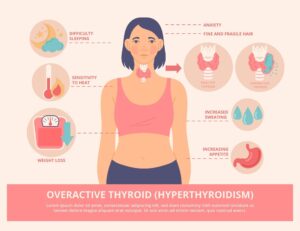
Hyperthyroidism manifests with a range of symptoms stemming from the overproduction of thyroid hormones. Common signs include rapid heart rate, weight loss despite increased appetite, anxiety, tremors, and excessive sweating.
Patients often experience fatigue, muscle weakness, and heat intolerance. Other symptoms may involve mood swings, insomnia, and changes in menstrual patterns. Additionally, hyperthyroidism can lead to physical manifestations such as bulging eyes (Graves’ ophthalmopathy) and a swollen, tender thyroid gland (goitre). Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of this thyroid disorder.
Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment
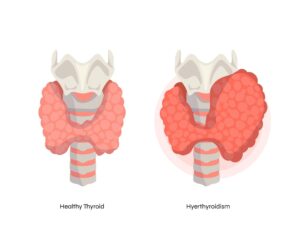
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism involves a series of medical assessments. Typically, blood tests measuring levels of thyroid hormones (T4 and T3) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) are conducted. Elevated T4 and T3 with suppressed TSH levels indicate hyperthyroidism.
A physical examination may reveal symptoms such as a swollen thyroid gland (goitre) or eye changes in Graves’ disease. Additionally, radioactive iodine uptake tests can pinpoint the cause, as different patterns of iodine absorption are associated with various thyroid conditions.
Hyperthyroidism Insomnia Treatment
Thyroid ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration may be used to evaluate nodules or goitres. Accurate diagnosis is pivotal in formulating an effective treatment for hyperthyroidism insomnia treatment
Hyperthyroidism treatment aims to reduce the production of thyroid hormones and alleviate the associated symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s age and overall health. Here are some of the primary approaches to managing hyperthyroidism:
- Antithyroid Medications: Methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU) are commonly prescribed medications that work by blocking the thyroid gland’s ability to produce hormones. These drugs are often used as initial treatment to control symptoms while the underlying cause is addressed. It’s essential to monitor thyroid hormone levels closely during this treatment.
- Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy: This treatment involves ingesting a radioactive form of iodine, which is absorbed by the overactive thyroid gland. The radiation gradually shrinks the gland and reduces hormone production. RAI therapy is highly effective but may lead to hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) in the long term, necessitating lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Thyroidectomy: In cases where medications and RAI therapy are ineffective or not recommended, surgical removal of the thyroid gland, known as a thyroidectomy, may be necessary. This procedure stops hormone production but needs lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
- Beta-Blockers: These medications, such as propranolol, help manage hyperthyroidism symptoms like rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety. They do not address the underlying cause but provide symptomatic relief.
Conclusion:
Hyperthyroidism treatment offers hope to those dealing with the challenges of an overactive thyroid gland. With the right approach, it is possible to restore balance to the body and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
If you suspect you have hyperthyroidism or are currently undergoing treatment, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure you receive the most appropriate and effective care for your specific needs.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
Difference Between Patent And Generic Medicine
The primary distinction between patent and generic medicines lies in their exclusivity and cost. A patent medicine is developed by a pharmaceutical company, offering them exclusive rights to sell it for a specified period, often around 20 years.
During this time, no other company can build the same drug. In contrast, generic medicines are identical copies of patent-expired drugs, offering the same quality and efficacy but at a lower cost since they can be produced by various manufacturers. This competition ultimately makes healthcare more affordable for consumers.
FAQs on Hyperthyroidism Treatment
Q1. What is hyperthyroidism treatment?
Hyperthyroidism treatment aims to reduce excessive thyroid hormone production. It includes antithyroid medications to inhibit hormone synthesis, radioactive iodine therapy to shrink the thyroid gland, or surgical removal of the thyroid (thyroidectomy) in severe cases. Treatment choice depends on factors like the underlying cause and individual health considerations.
Q2. What are the primary treatment options for hyperthyroidism?
The main treatment approaches include antithyroid medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy to shrink the thyroid gland and surgical removal of the thyroid (thyroidectomy) in severe cases.
Q3. Is hyperthyroidism treatment permanent, or will I need lifelong care?
The need for lifelong care depends on the chosen treatment method. Medications may require long-term use, while radioactive iodine treatment can lead to hypothyroidism, necessitating lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
Q4. Are there natural remedies or lifestyle changes that can complement hyperthyroidism treatment?
While medication, radioiodine, or surgery are the primary treatments, lifestyle changes like stress management, a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive iodine intake can support overall thyroid health and complement medical interventions.
Related Links:
