Last updated on April 22nd, 2025 at 06:08 pm
 Hernia treatment involves repairing the weakened abdominal wall or muscle through which an organ or tissue protrudes. This can be achieved through surgical procedures like laparoscopic or open surgery. The primary goal is to reposition the herniated tissue back into its proper place and reinforce the weakened area to prevent a recurrence. The choice of hernia treatment depends on factors like the type of hernia, its size, and the patient’s overall health.
Hernia treatment involves repairing the weakened abdominal wall or muscle through which an organ or tissue protrudes. This can be achieved through surgical procedures like laparoscopic or open surgery. The primary goal is to reposition the herniated tissue back into its proper place and reinforce the weakened area to prevent a recurrence. The choice of hernia treatment depends on factors like the type of hernia, its size, and the patient’s overall health.
Proper Treatment for Hernia aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Effective hernia treatment options are crucial for alleviating discomfort, preventing complications, and ensuring a patient’s overall well-being.
Hernia Treatment
The Treatment for Hernia is as follows:
1. Watchful Waiting:
In some cases, especially with small, asymptomatic hernias, doctors may recommend a “watchful waiting” approach. Regular monitoring is essential to detect any changes in the hernia’s size or symptoms. This approach is often suitable for elderly or high-risk patients.
2. Hernia Trusses:
Hernia trusses are supportive belts or devices designed to temporarily hold the hernia in place. However, they are typically not a permanent solution and may not be recommended for larger hernias. They can offer temporary relief for patients awaiting surgery or those who are not good candidates for surgery.
3. Laparoscopic Hernia Repair:
Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery has become a popular choice for hernia repair. It involves making small incisions and using a camera and specialized instruments to repair the hernia. Laparoscopic surgery typically results in shorter recovery times, reduced post-operative pain, and smaller scars compared to open surgery.
4. Open Hernia Repair:
In cases where laparoscopic repair is not feasible, open surgery remains a viable option. This approach involves making a larger incision at the hernia site, pushing the herniated tissue back into place, and reinforcing the abdominal wall with sutures or mesh. Open surgery is often used for complex hernias or in patients who may not tolerate laparoscopic procedures.
5. Hiatal Hernia Surgery:
Hiatal hernia repair aims to reposition the stomach and close the diaphragmatic opening. This can be done through open surgery or laparoscopically, depending on the patient’s condition and surgeon’s preference.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
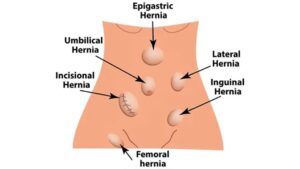
Types of Hernias
Hernias come in various forms, each characterized by its location and underlying cause. The most common types include inguinal hernias, which occur in the groin, and femoral hernias, located lower in the thigh.
Incisional hernias develop at prior surgical incision sites, while hiatal hernias involve the stomach pushing through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Umbilical hernias manifest near the navel, particularly in infants.
These hernias can vary in severity, with some causing mild discomfort and others requiring surgical intervention to prevent complications. Proper diagnosis and understanding of the type are essential for effective hernia treatment.
Causes of Hernias
Hernias have multiple causes, often involving a combination of factors. Weakness in the abdominal muscles due to age, genetics, or prior surgeries can create openings for hernias to occur. Heavy lifting, especially when done improperly, can strain the abdominal wall, increasing the risk of herniation.
Chronic constipation, which involves frequent straining during bowel movements, may stress abdominal muscles and contribute to hernias. Additionally, pregnancy can exert pressure on the abdominal wall, making women more susceptible.
Obesity, with its elevated intra-abdominal pressure, and persistent coughing or sneezing are other factors that can trigger hernias. Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention and timely Treatment of Hernia.
Inguinal Hernia Diagnosis And Treatment
Diagnosing an inguinal hernia typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Patients often report a visible or palpable bulge or discomfort in the groin area.
A healthcare provider will perform a thorough examination, asking the patient to cough or strain, which can make the hernia more noticeable. In some cases, additional tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis or assess the hernia’s size and severity.
The inguinal hernias treatment generally involves surgical intervention, as they do not tend to resolve on their own. The two primary approaches to hernia repair are open surgery and laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery.
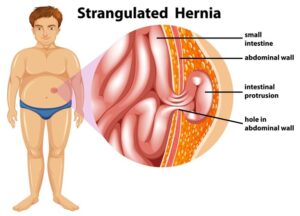
The choice of surgical technique depends on the patient’s circumstances, the hernia’s size and location, and the surgeon’s expertise. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of inguinal hernias are essential to prevent complications such as strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is compromised, which can be a medical emergency.
Conclusion:
Hernia treatment is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It requires a tailored strategy based on factors like hernia type, individual health, and surgeon expertise. With advances in surgical techniques and ongoing medical research, hernia treatment continues to evolve, offering patients improved outcomes and a quicker return to their normal lives. Consulting with a healthcare professional is the first step in finding the most suitable treatment plan for hernia management.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
Difference Between Generic and non generic Medicine
Generic medicines are equivalent to brand-name drugs but are typically more affordable. They contain the same active ingredients, dosage, and quality as their brand-name counterparts.
Non-generic or brand-name medicines, are often the original drugs developed by pharmaceutical companies and are usually more expensive due to research and marketing costs. The key distinction lies in the price and branding; generic drugs offer a cost-effective alternative without compromising on efficacy or safety.
FAQs on Hernia Treatment
Q1. What is hernia treatment?
Hernia treatment involves repairing the weakened muscle or tissue through which an organ protrudes. This can be achieved through surgical techniques, such as laparoscopic or open surgery, to reposition the herniated tissue and reinforce the abdominal wall. The choice of treatment depends on factors like hernia type, size, and the patient’s overall health.
Q2. Can hernias go away without treatment?
No, hernias do not typically resolve on their own. They often require surgical intervention to prevent complications.
Q3. What is the recovery time after hernia surgery?
Recovery time varies, but patients can usually return to light activities within a few weeks after laparoscopic surgery and several weeks after open surgery.
Q4. Are there non-surgical alternatives for Treatment for Hernia?
While hernia trusses can provide temporary support, they are not a long-term solution. Surgical repair remains the primary treatment for hernias.
Related Links: