Last updated on October 29th, 2024 at 05:34 pm
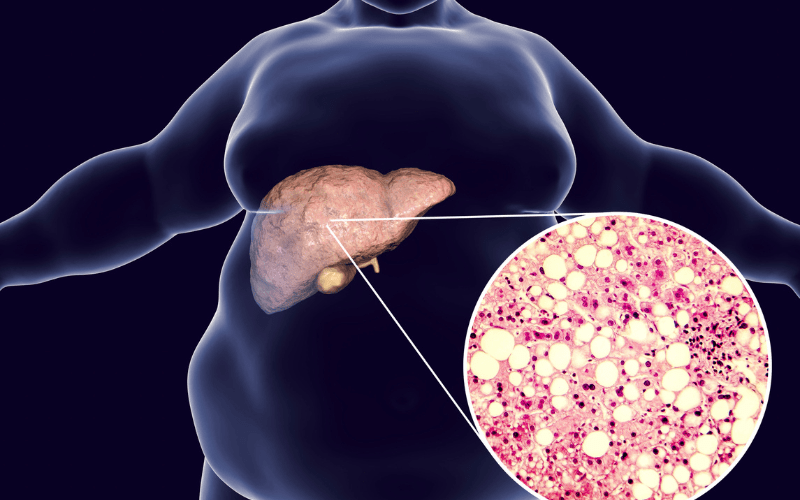
Fatty liver disease occurs when fat builds up inside the cells of the liver. This condition can range from mild to severe, and is categorized into three grades – grade 1, grade 2 and grade 3. Each grade is distinguished by the amount of fat present in the liver and the severity of the condition.
Introduction to Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells, which can lead to inflammation, scarring and liver damage. The most common form is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which occurs in people who do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol. NAFLD is often associated with other health conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol.

Fatty Liver Grade 1
Fatty liver Grade 1, also known as mild fatty liver, is a condition where there is a slight accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It is often diagnosed incidentally during routine medical check-ups, as it usually does not cause any symptoms.
Symptoms
Fatty liver Grade 1 usually does not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, in some cases, people may experience fatigue, weakness, or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen.
Causes
The exact cause of fatty liver grade 1 is not known, but it is often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol levels. Other risk factors include a sedentary lifestyle, a diet high in saturated fats and processed foods, and certain medications.
Prevention Techniques
The best way to prevent fatty liver grade 1 is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a balanced diet that is low in saturated fats and processed foods, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. It is also important to avoid alcohol and limit the use of certain medications that can cause liver damage.
Fatty Liver Grade 2
Fatty liver Grade 2, also known as moderate fatty liver, is a condition where there is a moderate accumulation of fat in the liver cells, which can lead to inflammation and scarring.
Symptoms
Fatty liver Grade 2 may cause symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen, and mild jaundice.
Causes
The causes of fatty liver grade 2 are similar to those of grade 1 fatty liver, and include obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol levels, a sedentary lifestyle, a diet high in saturated fats and processed foods, and certain medications.
Is Grade 2 Fatty Liver Dangerous?
Grade 2 fatty liver can lead to more serious complications if left untreated. It may lead to more serious liver conditions including cirrhosis or liver cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have grade 2 fatty liver.
Prevention Techniques
The prevention techniques for fatty liver grade 2 are similar to those for grade 1 fatty liver. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing fatty liver disease. It is also important to manage any underlying health conditions, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol levels.
Fatty Liver Grade 3
Fatty liver Grade 3, also known as severe fatty liver, is a condition where there is a significant accumulation of fat in the liver cells, which can lead to inflammation, scarring and liver damage.
Symptoms
Fatty liver Grade 3 may cause symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen, jaundice, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
Causes
The causes of Fatty liver grade 3 are similar to those of grade 1 and 2 fatty liver, and include obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol levels, a sedentary lifestyle, a diet high in saturated fats and processed foods, and certain medications.
Prevention Techniques
The prevention techniques for fatty liver grade 3 are similar to those for grade 1 and 2 fatty liver. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing fatty liver disease. It is also important to manage any underlying health conditions, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol levels.
Life Expectancy with Fatty Liver Disease
The life expectancy depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of other health conditions. In general, people with mild to moderate fatty liver disease have a good prognosis, while those with severe may have a shorter life expectancy.

Conclusion:
Millions of people all around the world suffer from the common condition known as fatty liver disease. It is categorized into three grades – grade 1, grade 2 and grade 3 – each with its own set of symptoms, causes and prevention techniques. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying health conditions are key to preventing fatty liver disease. It is important to seek medical attention to prevent serious complications.
FAQs on Understanding Grade 1, 2 and 3 Fatty Liver
Q1. Are there any specific dietary recommendations for preventing fatty liver disease?
Answer : Maintaining a healthy diet is essential for preventing fatty liver disease. A diet low in saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods, and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help prevent the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Q2. Are there any specific exercises that can help prevent or manage fatty liver disease?
Answer : Regular exercise, especially aerobic exercise such as walking, jogging, or swimming, can help prevent and manage fatty liver disease. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss, and reduces fat accumulation in the liver.
Q3. Can fatty liver disease affect children?
Answer : It can affect children, especially those who are overweight or obese. This condition, known as pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is becoming increasingly common and can lead to serious health problems if not addressed.
