Last updated on May 20th, 2025 at 12:40 pm

The normal range for fasting blood sugar, a key indicator of glucose regulation, typically falls between 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). This measurement is obtained after an overnight fast and serves as a crucial baseline for assessing one’s metabolic health. Values within this range indicate effective glucose control, while consistently elevated levels may suggest conditions such as insulin resistance or diabetes.
Regular monitoring, coupled with a healthy lifestyle emphasizing balanced nutrition and physical activity, is essential for maintaining optimal fasting blood sugar levels and preventing potential health complications. If values deviate from this range, consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for further evaluation and personalized guidance.
Regular Blood Sugar Range in Fasting
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle involves keeping a close eye on various health indicators, and one crucial parameter is fasting blood sugar levels. Fasting blood sugar (FBS) is a measure of the amount of glucose present in your blood after an overnight fast. Understanding the normal range of fasting blood sugar is essential for monitoring your overall health and preventing the onset of conditions like diabetes.
Fasting blood sugar is a key indicator of your body’s ability to regulate glucose levels. Glucose, derived from the food we eat, serves as the primary source of energy for our cells. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, maintaining blood sugar within a normal range.
A fasting blood sugar test is typically done after an overnight fast or at least 8 hours without food. This baseline measurement provides valuable insights into your body’s glucose regulation and helps identify potential issues such as insulin resistance or diabetes.
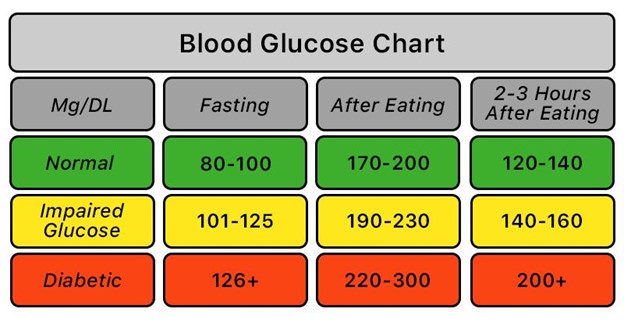
Classification
The normal levels can vary slightly among different healthcare organizations, but they generally fall within the range of 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Here’s a breakdown of the classifications:
- Normal : 70-100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose) : 101-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes : 126 mg/dL or higher
It’s important to note that these values are general guidelines, and individual variations may exist. Additionally, factors such as age, medical history, and other health conditions can influence fasting blood sugar levels.
Also, Read:
- BP Normal Range for Female
- Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
- Diet Plan For Weight Loss
- How to Lose Weight Fast?
- How To Reduce Belly Fat
Significance of Monitoring Fasting Blood Sugar
Maintaining fasting blood sugar within the normal range is crucial for overall health. Consistently elevated levels may indicate insulin resistance or diabetes, both of which can lead to serious health complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage.
Regular monitoring of fasting blood sugar is especially important for individuals with a family history of diabetes, those who are overweight, and individuals with sedentary lifestyles. Early detection of abnormal levels allows for timely intervention, often through lifestyle changes like adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and, in some cases, medication.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Fasting Blood Sugar Range
The tips and tricks for maintaining a healthy fasting blood sugar level normal range are mentioned below:
1. Balanced Diet
Consume a well-balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Limit the intake of refined sugars and processed foods.
2. Regular Exercise
Incorporate consistent physical activity into your routine to enhance insulin sensitivity and maintain optimal blood sugar levels. Strive for a minimum of 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity exercise to promote overall well-being.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly contribute to optimal blood sugar control.
4. Regular Monitoring
If you have risk factors for diabetes or other metabolic conditions, discuss regular blood sugar monitoring with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Understanding the normal range of fasting blood sugar is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing the development of chronic conditions like diabetes. Regular monitoring, coupled with a healthy lifestyle, can contribute to optimal blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications. If you have concerns about your fasting blood sugar levels, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and recommendations tailored to your individual health needs.
FAQs on Fasting Blood Sugar Normal Range
Q1. What is the blood sugar normal range while fasting?
The normal range for fasting blood sugar is typically between 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Values below 70 mg/dL may indicate hypoglycemia, while levels above 100 mg/dL may suggest impaired fasting glucose or diabetes. Regular monitoring and maintaining levels within this range are crucial for overall health.
Q2. What is considered a normal fasting blood sugar range?
The normal range for fasting blood sugar is generally between 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Values outside this range may indicate potential health concerns.
Q3. What should I do if my fasting blood sugar levels are consistently high?
Consult with a healthcare professional if your fasting blood sugar consistently exceeds 100 mg/dL, as it could indicate conditions like insulin resistance or diabetes. Lifestyle changes and medical intervention may be recommended.
Related Links: