Last updated on July 2nd, 2025 at 05:36 pm

Skin infections are widespread conditions caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, affecting people of all ages and skin types. The skin, as the body’s first line of defense, is constantly exposed to various pathogens, making it vulnerable to infections, especially when it is damaged or compromised. These infections can range from mild irritations to severe conditions that require medical attention. Common symptoms are redness, itching, rashes, swelling, and in some cases, blisters or pus-filled bumps.
Factors like poor hygiene, weakened immune systems, excessive sweating, or exposure to contaminated environments can increase the risk. Whether it’s a viral wart, a fungal athlete’s foot, or a bacterial impetigo, recognizing the early signs of a skin infection is crucial for timely treatment. With proper care, most skin infections can be effectively managed, reducing the risk of complications or spreading to other parts of the body.
Types of Skin Infections
There are four main types of skin infections:
1. Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacterial infections often begin as small red bumps that resemble skin allergy and gradually increase in size. Examples include cellulitis, impetigo, and boils. These infections are usually caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus and Streptococcus.
2. Viral Skin Infections
Viral skin infections are caused by viruses like the herpes virus, human papillomavirus (HPV), and the poxvirus. Common viral skin infections include warts, cold sores, and shingles. These infections often have characteristic symptoms like blisters, itching, or painful sores.
3. Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections thrive in moist and warm environments, making areas like the feet, armpits, and groin particularly vulnerable. Fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections.
4. Parasitic Skin Infections
Parasitic infections are caused by tiny organisms like lice, mites, and bedbugs. They typically result in itching, rashes, and sometimes even allergic reactions. Examples include scabies and lice infestations.
Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal infections are among the most prevalent types of skin infections. Reason for fungal infection is that they invade the skin, thriving in areas that are damp and poorly ventilated. Some fungal infections can be superficial, while others may penetrate deeper into the skin.
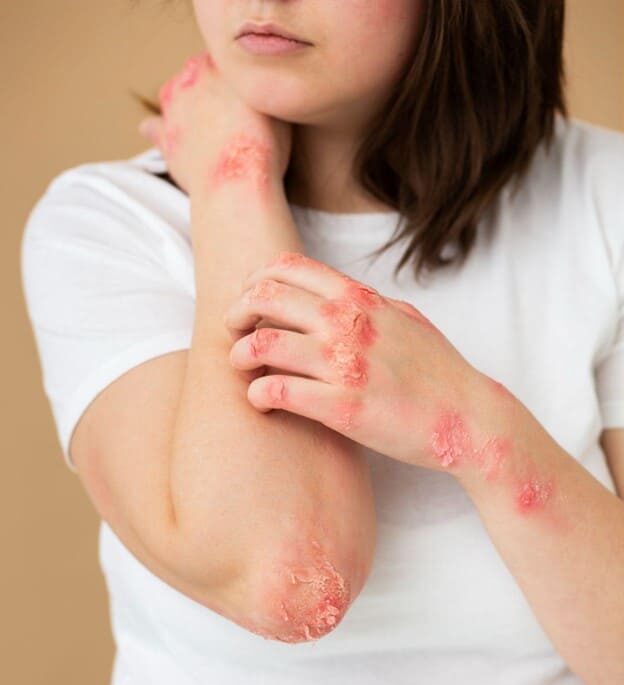

Common Types of Fungal Skin Infections
1. Ringworm (Tinea)
This is a common fungal skin infection that presents with a circular, red rash. It can appear anywhere on the body, including the scalp, feet (athlete’s foot), or groin (jock itch).
2. Candidiasis
Caused by Candida yeast, this infection commonly occurs in moist areas of the body like the armpits, under the breasts, and the groin. It may also affect the mouth (oral thrush).
3. Fungal Infection on Black Skin
Fungal infections may present differently depending on skin tone. For instance, fungal infections on black skin often result in hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation (lighter or darker skin patches). This can make fungal infections harder to diagnose visually on darker skin tones.
Symptoms of Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections can present a variety of symptoms depending on the type and location of the infection. Common symptoms include a red, scaly rash that may itch or burn. Infections like ringworm cause circular, raised patches with a clearer center, while athlete’s foot may result in cracked, peeling, or flaky skin between the toes. In areas such as the groin, fungal infections can appear as reddish or brownish patches with distinct edges. On black skin, infections can cause hyperpigmentation (darker patches) or hypopigmentation (lighter patches), making diagnosis more challenging.
Other symptoms include:
– Itching, often intense
– Blisters or sores, especially in moist areas
– Dry, flaky skin or scaling
– White or discolored patches, especially in infections like tinea versicolor
Yellow Fungus Symptoms
Yellow fungus is a rare but severe fungal infection, often more dangerous than other fungal infections like white or black fungus. Its symptoms include extreme lethargy, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, and slow wound healing. In advanced stages, it can cause pus leakage, sunken eyes, and necrosis (tissue death), leading to severe internal damage. Unlike other fungal infections, yellow fungus starts internally, making early detection difficult. The infection requires immediate medical intervention, often with antifungal medications such as amphotericin B. Delayed treatment can result in life-threatening complications, making early diagnosis critical.
Reason for Fungal Infection
– Warm and humid environments
– Sweating excessively
– Poor hygiene
– Wearing tight, damp clothing
– Weak immune system
– Using antibiotics, which can kill good bacteria and allow fungi to flourish
Treatment for Fungal Infections
The treatment for fungal infections depends on the type of fungus and its severity. Here are some options:
1. Medicine for Fungal Infection on Skin
Antifungal infection creams, powders, or oral medications are commonly used. Over-the-counter antifungal medications like clotrimazole or miconazole can help clear up mild infections. In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications such as fluconazole or terbinafine.
2. How to Cure Fungal Infection on Skin Naturally at Home
Some natural remedies can help soothe and manage fungal infections at home:
– Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, applying diluted tea tree oil can help reduce fungal infections.
– Garlic: Garlic has natural antifungal properties. Crushing garlic and applying it to the infected area can help, although it might cause some irritation.
– Apple Cider Vinegar: Soaking the infected area in diluted apple cider vinegar can help balance the skin’s pH and reduce fungal growth.
– Aloe Vera: This soothing gel can reduce irritation and inflammation caused by fungal infections while also inhibiting fungal growth.
Viral Skin Infections
Viral skin infections are contagious and can range from mild to severe. These infections can affect different parts of the skin and are often accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or body aches.
Common Types of Viral Skin Infections
1. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
This virus causes cold sores (HSV-1) and genital herpes (HSV-2). It presents as fluid-filled blisters that are often painful and contagious.
2. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
This virus causes warts, including common warts, plantar warts, and genital warts. Warts appear as rough, thickened areas of skin and can spread from person to person.
3. Chickenpox and Shingles
Both are caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Chickenpox is common in children, while shingles is a reactivation of the virus in older adults, causing painful blisters.
Symptoms of Viral Skin Infections
– Fluid-filled blisters or sores
– Pain, itching, or burning sensations
– Skin rashes
– Fever or body aches (in more severe cases)
Treatment for Viral Skin Infections
Viral infections often clear up on their own, but antiviral medications may be prescribed to reduce the severity and duration of the infection. For instance, acyclovir is commonly used to treat HSV infections. Keeping the affected area clean and dry is also essential to prevent the spread of infection.
Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacterial skin infections occur when harmful bacteria, such as Staphylococcus or Streptococcus, invade the skin. Common causes include cuts, scrapes, insect bites, or other skin injuries that allow bacteria to enter. Poor hygiene, weakened immunity, or underlying health conditions also increase the risk. Symptoms of bacterial infections can range from redness, swelling, and warmth at the infection site to pus-filled bumps or sores. Examples include cellulitis, impetigo, and boils. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, either topical or oral, depending on the severity of the infection. Keeping the infected area clean and dry is crucial, and severe infections may require medical drainage or other interventions to prevent complications. Early treatment helps prevent the infection from spreading.
In cases of severe skin inflammation caused by allergic reactions or autoimmune conditions, medications like Omnacortil Oral Solution 60 ml and Eqoq Tablet 10s may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress immune response.
Prevention Tips for Skin Infections
Preventing skin infections involves practicing good hygiene and taking precautions in environments where infections are common, such as gyms and swimming pools.
Here are some tips:
– Wash your hands regularly with soap and water.
– Keep your skin clean and dry, especially in areas prone to sweat.
– Avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, or clothing.
– Wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable materials.
– Treat cuts, scrapes, and insect bites promptly to prevent infection.
– Strengthen your immune system with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Conclusion
Skin infections can range from mild annoyances to serious health issues, but most can be treated effectively with proper care. Recognizing the symptoms early and taking immediate steps—whether using antifungal medication, natural remedies, or antiviral treatments—can significantly improve recovery and prevent the spread of infection. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment if symptoms persist or worsen.
FAQs On Common Skin Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
1. What are the common causes of skin infections?
Skin infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Factors like poor hygiene, a weakened immune system, and prolonged exposure to damp environments increase the risk. Cuts, scrapes, or insect bites also provide entry points for pathogens.
2. What is the best antifungal cream for private area?
Clotrimazole-based creams, such as Canesten, are commonly recommended for treating fungal infections in private areas due to their broad-spectrum efficacy and availability. Miconazole nitrate creams, like Monistat, are also effective and widely used. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable fungal infection cream based on the specific infection.
3. How are skin infections treated?
Treatment depends on the type of infection. Bacterial infections are typically treated with antibiotics, while antifungal creams or oral medications handle fungal infections. Viral infections usually resolve on their own, though antiviral drugs may be prescribed for more severe cases.
4. What are the symptoms of White Fungus?
White fungus infections can cause persistent cough, fever, chest pain, and breathing difficulties, especially if it spreads to the lungs. In severe cases, it may affect other organs, leading to symptoms like swelling, fatigue, and localized pain. The infection can also result in white patches on the skin or mucous membranes.
Related Links :