Last updated on December 20th, 2024 at 12:55 pm
Cellulitis treatment primarily involves antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection. Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can affect any part of your body, although it most commonly occurs on the legs and face. It typically begins as a red, swollen area that feels warm to the touch. As the infection progresses, it can cause fever, chills, and pain.
Cellulitis is usually caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus bacteria, which can enter your body through a break in the skin, such as a cut, scrape, or insect bite. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity and causative bacteria. Pain relievers may be used for comfort for cellulitis treatment. Elevating the affected area can reduce swelling. Rest, hydration, and wound care are essential.
In instances of extreme severity, hospitalisation and the administration of intravenous antibiotics may become imperative. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for effective cellulitis treatment.
Cellulitis Diagnosis and Treatment
Cellulitis diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider who assesses the affected skin area for redness, warmth, tenderness, and swelling. Medical history, including recent skin injuries or infections, is also considered.
In some cases, a culture of the affected skin may be taken to identify the specific bacteria responsible. Imaging tests like ultrasounds or MRIs might be ordered to assess the extent of infection or rule out other underlying conditions.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential to initiate appropriate treatment promptly and prevent cellulitis from worsening or leading to complications.
Cellulitis Treatment
The Treatment of Cellulitis is as follows:
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the cornerstone of cellulitis treatment. Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection. The choice of antibiotic may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria responsible.
It’s crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before you finish the medication. Stopping antibiotics prematurely can allow the bacteria to become resistant to the drugs.
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate the discomfort associated with cellulitis.
Elevation
Elevating the affected limb, such as your leg or arm, can help reduce swelling and discomfort. Keep the area elevated whenever possible, especially when resting.
Rest and Hydration
Resting and staying hydrated can aid in your body’s recovery process. Adequate rest allows your immune system to work efficiently, while hydration helps flush toxins from your body.
Wound Care
Proper wound care is essential to prevent cellulitis from recurring. Keep any cuts, scrapes, or other skin injuries clean and covered with a sterile dressing. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care, which may include cleaning the area with mild soap and water, applying antibiotic ointment, and keeping it covered with a bandage.
Surgical Drainage (in some cases)
If an abscess forms within the infected area, your doctor may need to drain it surgically to remove the pus and alleviate pressure.
> Consult a Doctor and Medkart will help you Order Medicines Online
Cellulitis Treatment at Home – Cellulitis Leg Treatment
Cellulitis of the leg is typically treated with a course of oral antibiotics, with a specific choice of antibiotic depending on the severity and causative bacteria. Elevating the affected leg, maintaining good hygiene, and keeping the area clean and covered are essential steps.
Pain management may include over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers. In severe cases, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics might be necessary. Prompt treatment is vital to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for the most effective cellulitis leg treatment.
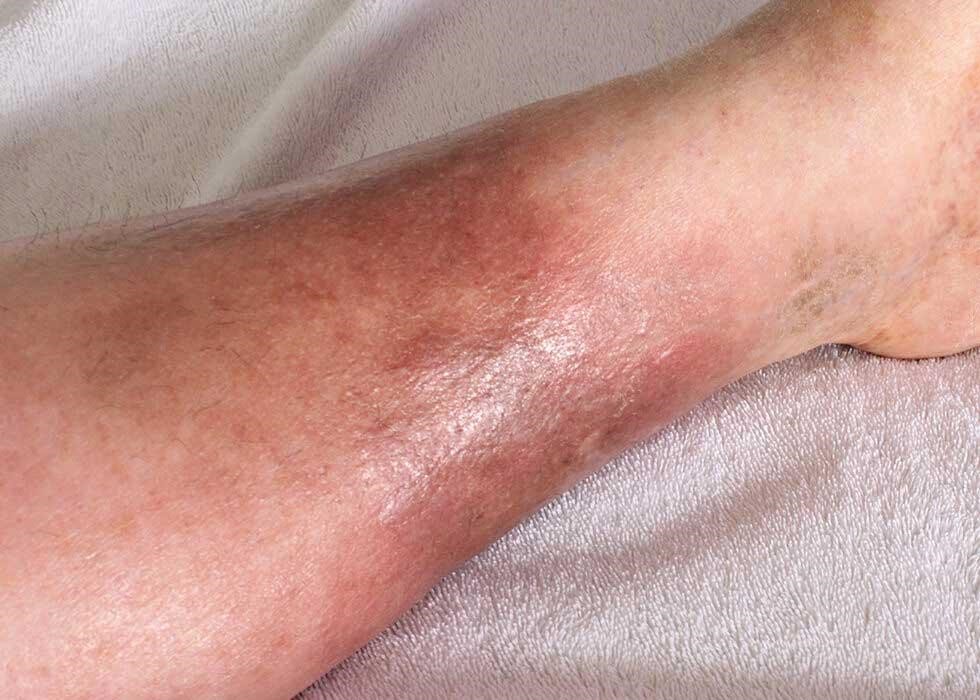
Cellulitis Home Treatment
While cellulitis often requires medical intervention, certain home-care practices can complement treatment. Rest and elevation can reduce swelling and discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers help manage pain and fever.
Keep the affected area clean, apply antibiotic ointment, and cover it with a sterile bandage. Staying well-hydrated and completing prescribed antibiotics are essential.
However, home treatment should not replace professional medical care, and seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for proper cellulitis management and prevention of complications.
Conclusion:
Cellulitis is a treatable skin infection that should not be ignored. Timely medical intervention, including antibiotics and proper wound care, is key to a successful recovery and preventing complications. If you suspect you have cellulitis or notice any signs of infection, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Remember that prevention is just as important as treatment. Take steps to protect your skin from injuries and practice good hygiene to reduce your risk of developing cellulitis in the first place. With the right treatment and care, you can quickly overcome cellulitis and get back to enjoying a healthy, active life.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
Do Generic Medicines work the same?
Yes, generic medicines work the same as brand-name counterparts in terms of safety, efficacy, and quality. They contain the same active ingredients, have the same intended use, and meet the same rigorous standards set by regulatory authorities.
Generic drugs may have slight differences in non-active ingredients, such as fillers or binders, which do not affect their performance. These cost-effective alternatives provide the same therapeutic benefits, making them a reliable option for many patients.
Always consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist for advice on switching to generics.
FAQs on Cellulitis Treatment
Q1. What is cellulitis treatment?
Cellulitis home treatment involves prescribed oral antibiotics, rest, and elevation of the affected area. Keep the area clean, apply antibiotic ointment, and cover it with a sterile bandage. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper guidance and to ensure the infection doesn’t worsen.
Q2. Can cellulitis be treated at home?
Mild cases may be managed at home with prescribed antibiotics and proper wound care, but it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Q3. How long does cellulitis treatment typically last?
The duration of cellulitis treatment with antibiotics is typically 7 to 14 days, but it can vary depending on the severity and individual response to medication.
Q4. What should I do if my cellulitis doesn’t improve with treatment?
If you see no improvement or experience worsening symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately, as it may require a change in antibiotics or further evaluation for complications.
Related Links:
