Last updated on July 14th, 2025 at 11:15 am
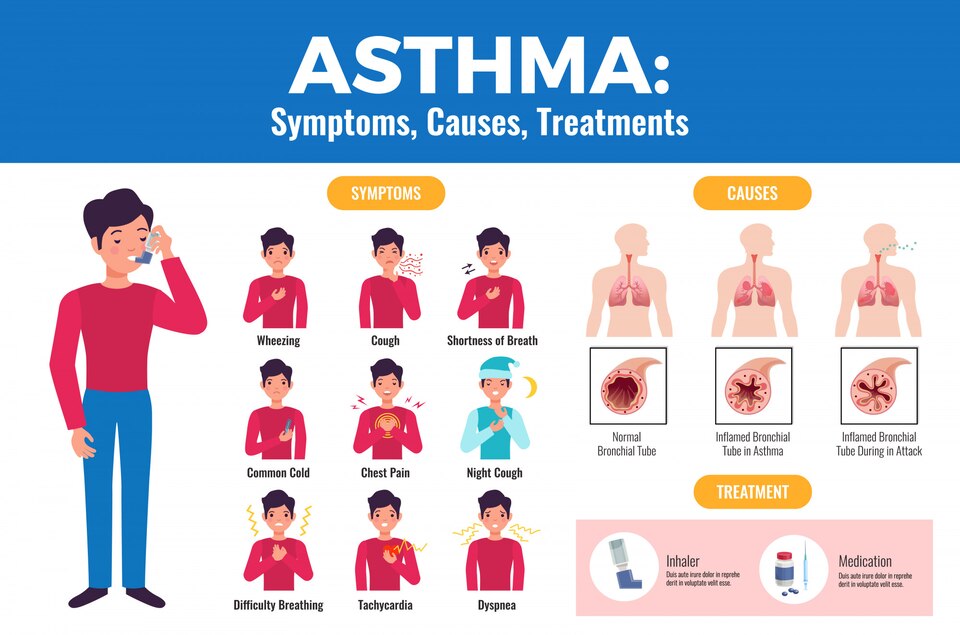
 Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition indicated by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, impacting millions of people worldwide. Managing and treating bronchial asthma is crucial to ensure a high quality of life for those afflicted with the condition. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of bronchial asthma treatment, from medications to lifestyle changes, with a focus on promoting respiratory wellness.
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition indicated by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, impacting millions of people worldwide. Managing and treating bronchial asthma is crucial to ensure a high quality of life for those afflicted with the condition. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of bronchial asthma treatment, from medications to lifestyle changes, with a focus on promoting respiratory wellness.
Asthma Treatment Medications
1. Bronchodilators:
These drugs help relax and open the airways, providing quick relief during asthma attacks. Short-acting bronchodilators like albuterol are used for acute symptoms, while long-acting bronchodilators are employed for long-term control.
2. Inhaled Corticosteroids:
These anti-inflammatory medications help reduce airway inflammation, preventing asthma symptoms. Common examples include fluticasone and budesonide.
3. Leukotriene Modifiers:
These medications block the action of leukotrienes, which contribute to airway inflammation. Montelukast is a well-known leukotriene modifier.
4. Combination Inhalers:
Some medications combine both bronchodilators and corticosteroids to provide comprehensive asthma control. Examples include Advair and Symbicort.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
5. Allergen Management
Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers is vital. Allergens such as dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and mould can exacerbate bronchial asthma symptoms. Reducing exposure to these allergens through measures like allergen-proof covers, air purifiers, and regular cleaning can be beneficial.
6. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major asthma trigger and should be avoided. Smoking cessation programs and support are essential for individuals with bronchial asthma who smoke.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve lung function and overall health. However, individuals with bronchial asthma should work with their healthcare providers to develop an exercise plan that suits their condition and may require pre-exercise bronchodilator use.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and potentially reduce asthma flare-ups.
 Bronchial Asthma Action Plan
Bronchial Asthma Action Plan
Patients with bronchial asthma should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized asthma action plan. This plan outlines medication use, asthma triggers, and steps to take during an asthma attack.
1. Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
- Regular monitoring of lung function through peak flow meters or spirometry is crucial to assess asthma control.
- Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers ensure that treatment plans are adjusted as needed to maintain optimal asthma control.
2. Emergency Treatment
In severe cases or during asthma exacerbations, immediate medical attention may be required. Hospitals are equipped to administer oxygen, intravenous medications, and other treatments to alleviate severe symptoms.
Childhood Asthma Treatment
Childhood asthma is a common chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of children worldwide. Effective management and treatment of childhood asthma are essential to ensure that young ones can lead active, healthy lives.
1. Medications
- Quick-Relief Medications: Short-acting bronchodilators, such as albuterol, are often prescribed to provide immediate relief during asthma attacks or when symptoms worsen suddenly.
- Long-Term Control Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and long-acting bronchodilators are commonly used to reduce airway inflammation and prevent asthma symptoms from occurring in the first place.
- Combination Inhalers: Some medications combine both bronchodilators and corticosteroids to provide comprehensive asthma control, which can be particularly useful in children with moderate to severe asthma.
If asthma symptoms are accompanied by a wet cough or mucus build-up, supportive syrups like Ascoril LS Syrup/Relent Plus Syrup may be recommended to loosen phlegm and improve breathing comfort.
> Consult a doctor and Order Medicine Online
2. Allergen Management
Identifying and avoiding allergens that trigger asthma in children is crucial. Common allergens include dust mites, pollen, pet dander, mould, and tobacco smoke. Parents should take steps to minimize exposure to these triggers, such as using allergen-proof bedding and maintaining a smoke-free environment.
3. Lifestyle and Environmental Adjustments
- Encouraging Physical Activity: Physical activity is important for children’s overall health. Parents should work with healthcare providers to create an exercise plan that accommodates the child’s asthma and ensure they have a rescue inhaler available during activities.
- Healthy Diet: Proper nutrition supports lung development and immune function. A well-balanced diet can help children with asthma stay healthier.
- Managing Stress: While it may not be as pronounced in children as in adults, stress can still affect asthma symptoms. Creating a calm and supportive environment can help reduce stress for children with asthma.
4. Asthma Action Plan
Parents, caregivers, and schools should work together to create a personalized asthma action plan for each child with asthma. This plan outlines medication usage, asthma triggers, and steps to take in case of an asthma attack. It is crucial that teachers and school staff are aware of these plans to provide appropriate support.
5. Regular Monitoring and Check-ups
Parents should monitor their child’s lung function using peak flow meters or other tools recommended by their healthcare provider. Regular check-ups with the paediatrician or asthma specialist are essential to assess asthma control and make necessary treatment adjustments.
6. Education and Support
Providing children with age-appropriate information about their asthma and how to manage it empowers them to take an active role in their treatment.
Support groups and resources are available to help parents and children better understand asthma and connect with others facing similar challenges.
Childhood asthma treatment is a collaborative effort involving parents, caregivers, healthcare providers, and schools. By following a comprehensive treatment plan that includes medication management, allergen control, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring, children with asthma can thrive and enjoy a healthy, active childhood. It’s essential for parents and caregivers to be well-informed about childhood asthma and work closely with healthcare professionals to provide the best care for their young ones’ growing lungs.
Conclusion:
Bronchial asthma treatment is a multifaceted approach that combines medications, allergen management, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring. By working closely with healthcare providers and following a personalized asthma action plan, individuals with bronchial asthma can effectively manage their condition, reduce symptoms, and enjoy an improved quality of life. It is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in asthma treatment to ensure the best possible care for this chronic respiratory condition.
FAQs On Asthma Treatment
Q.1 What is Asthma Treatment?
Asthma treatment refers to the medical interventions and strategies used to manage and alleviate the symptoms of asthma, a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. The primary goals of asthma treatment are to control symptoms, prevent asthma attacks, improve lung function, and enable individuals with asthma to lead a normal, active life.
Q2. Can asthma be cured with treatment, or is it a lifelong condition?
Asthma is a chronic condition, which means it is typically not curable. However, with proper treatment and management, most individuals with asthma can lead normal, symptom-free lives. Treatment aims to control symptoms, prevent asthma attacks, and improve lung function, allowing individuals to live without significant limitations.
Q3. What lifestyle changes can complement asthma treatment?
Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in asthma management. Some recommended changes include avoiding known asthma triggers (e.g., allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander), quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity (with appropriate precautions), and managing stress. These changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of asthma symptoms and improve overall lung health.
Related Links: