Managing blood sugar is important for overall health, especially for those at risk of or living with diabetes. Understanding normal glucose levels after eating, also known as postprandial glucose levels, is a key part of this process.
What Are Normal Glucose Levels?
Normal glucose levels are described as the concentration of glucose in the blood. Glucose is an essential source of energy for the body, but proper levels must be maintained not to cause a problem. A range for normal blood glucose varies based on several factors, including age, activity level, and the timing after a meal.
Fasting vs. Postprandial Glucose Levels
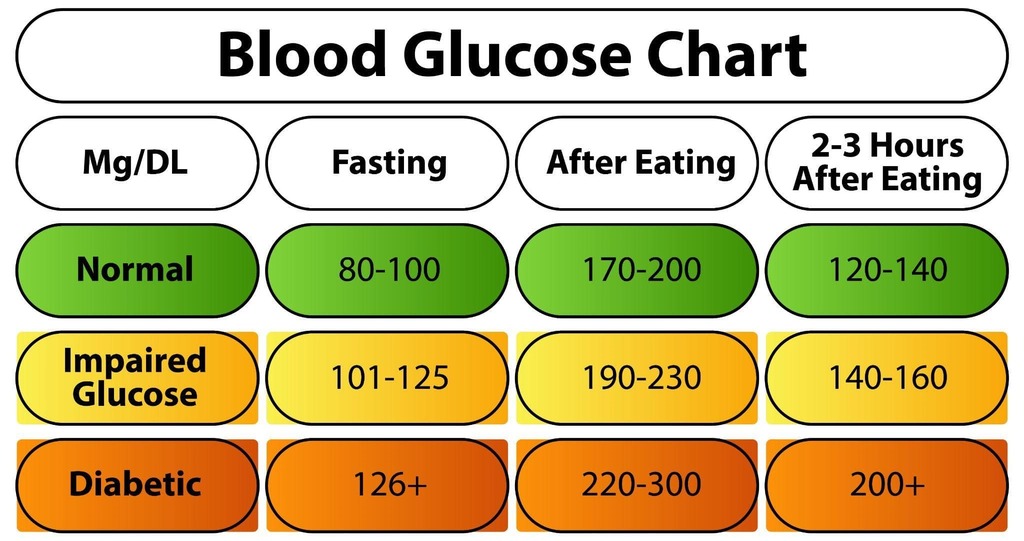
- Fasting Glucose Levels: This is the measurement of blood sugar levels after not eating for at least 8 hours. The normal range is usually between 70–100 mg/dL for healthy individuals.
- Blood Sugar Levels After Food (Postprandial): This is the time when glucose levels increase due to the digestion of food. The normal sugar level after food for most healthy adults is less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. However, this varies with age and general health.
Why Monitor Blood Sugar Levels After Food?
Monitoring your blood sugar level after food provides insights into how your body processes glucose. A consistently high level may indicate insulin resistance or diabetes, while low levels could point to hypoglycemia. Understanding your body’s response to meals helps in managing your diet and preventing complications.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Adults
For adults without diabetes, the normal range for glucose levels is as follows:
Fasting Glucose Levels: 70–100 mg/dL
Random Blood Sugar Normal Range: Lower than 140 mg/dL
Blood Sugar Level After Food (2 hours after eating): Lower than 140 mg/dL
A normal blood sugar levels chart can be used to keep track of these values and to make comparisons with standard ranges. A person with diabetes may have more elevated target ranges, which should be determined by a healthcare provider.
Factors That Affect Postprandial Glucose Levels
Several factors affect your normal sugar level after food:
Meal Composition: Carbohydrate- or sugar-rich foods lead to an increase in blood glucose.
Physical Activity: Insulin sensitivity increases with regular physical activity, thereby keeping blood glucose within normal ranges.
Timing of Meals: Irregular meal times interfere with your body’s glucose control.
Age: Elderly people may have higher glucose levels after eating.
Health Conditions: Diseases like diabetes or insulin resistance affect how the body uses glucose.
How to Maintain Normal Sugar Levels After Food
To keep your normal blood sugar levels for adults within the healthy range, consider the following tips:
- Balanced Diet: Concentrate on a diet with high fiber, lean proteins, and good fats. Stay away from processed sugars and refined carbohydrates.
- Portion Control: Eat smaller meals at more frequent intervals to prevent spikes in blood sugar.
- Check regularly: Use a glucometer to measure your blood sugar after food and track patterns.
- Stay Active: Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and keeps glucose levels in check.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support metabolic processes and glucose regulation.
The Importance of Maintaining Normal Glucose Levels
Glucose is the major sugar that circulates in your blood. Its role is to provide energy for your body, but the normal range is of utmost importance in maintaining a good health condition. Whether fasting, eating, or at any time of the day, maintaining normal glucose levels prevents chronic diseases, helps improve daily functioning, and contributes to a longer life span.
Key Reasons Why Normal Glucose Levels Matter
1. Energy and Cellular Function
Glucose is the body’s primary fuel for energy, powering both the movement of your body and the functioning of your brain. Steady normal blood glucose levels ensure your cells get the energy they need without overwhelming your system.
2. Prevention of Chronic Conditions
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over time can cause prediabetes or diabetes, which brings your risk factor for heart disease, kidney damage, nerve problems, and vision loss to a whole new level.
Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia occurs when your blood glucose level falls below the normal range, causing dizziness, confusion, fainting, or even seizures.
Maintaining your glucose level can prevent these complications and ensure you enjoy a quality life.
3. Healthy Cardiovascular System
High glucose levels damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of hypertension, stroke, and heart disease. A normal sugar level protects your cardiovascular system and promotes long-term health.
4. Improved Mental Function
The brain requires glucose as a source of energy. Maintaining stable glucose levels enhances concentration, memory, and the overall sharpness of one’s mind. Deviations from normal adult blood sugar may eventually cause brain fogginess or cognitive dysfunction.
5. Improved Physical Activity
Well-regulated normal blood glucose levels enable muscles to work more effectively for longer periods, greatly enhancing endurance and recovery from the endeavours of physical activities. High blood sugar spikes and crashes may cause fatigue or drowsiness during exercise.
Lifestyle Advantages of Normal Glucose Levels
- Healthy Weight: Blood glucose stability decreases cravings or overeating, and overall, it becomes easy to manage weight.
- Insulin Function: Within the normal range, insulin acts more efficiently to maintain glucose, which further helps in other hormonal functions in one’s body.
- Longevity: Tight glucose control has been linked to a reduced risk of age-related diseases, thus extending life and enhancing its quality.
Understanding Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
If your glucose levels fall outside the normal blood glucose level range, it is essential to determine the cause:
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): This may be a sign of diabetes, stress, or a lack of an appropriate insulin response.
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Often caused by skipping meals, excessive insulin, or extended periods of exercise.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Here is a table outlining normal blood sugar levels for different age groups, including before eating (fasting), after eating (postprandial), and random levels:
|
Age Group |
Fasting Glucose Levels |
2 Hours After Eating (Postprandial) |
Random Blood Sugar |
|
Children (Under 6) |
80–100 mg/dL |
Less than 140 mg/dL |
100–180 mg/dL |
|
Children (6–12) |
80–100 mg/dL |
Less than 140 mg/dL |
90–180 mg/dL |
|
Teens (13–19) |
70–100 mg/dL |
Less than 140 mg/dL |
90–150 mg/dL |
|
Adults (20–59) |
70–100 mg/dL |
Less than 140 mg/dL |
Less than 140 mg/dL |
|
Older Adults (60+) |
80–110 mg/dL |
Less than 160 mg/dL |
Less than 150 mg/dL |
Notes:
These ranges serve as general recommendations for healthy nondiabetic persons with no complications in glucose homeostasis.
Random blood glucose: This represents values obtained at any time during the day regardless of meals
Individuals with diabetes or with specific diseases would have different targets. Always see a healthcare provider for professional recommendations
Older adults may need a higher target value to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
Conclusion
Understanding and maintaining normal blood glucose levels is important for long-term health. By monitoring your blood sugar level after food and healthy habits, you prevent complications such as diabetes and can maintain your energy levels throughout the day. You can use a normal blood sugar levels chart for information and talk to a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Whether you’re managing a health condition or simply aiming for better wellness, keeping your glucose levels within the normal blood sugar levels for adults range is a powerful step toward achieving your goals.
FAQs on What Are Normal Glucose Levels After Eating?
1. What is the normal blood sugar level after eating?
The normal level of blood glucose after a meal, referred to as the postprandial glucose level, is below 140 mg/dL two hours after the time someone eats in healthy people. The values may vary among patients with diabetes or other related diseases. These are held at proper levels through frequent checks and an appropriate diet.
2. When can the blood sugar level start measuring postprandium?
Postprandial glucose is usually checked two hours after eating for blood sugar levels. It allows enough time for food to be digested and glucose to enter the bloodstream. Monitoring at this time helps assess how well your body processes sugar.
3. Why do blood sugar levels rise after eating?
After consuming, your body metabolizes carbohydrates into glucose, which gets absorbed into the bloodstream. As a result, there is an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood. Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, facilitates glucose to enter the cells to provide energy, thereby normalizing the levels.
4. What are the determinants of postprandial glucose?
All these factors can influence postprandial glucose, including meal composition (high-carb or sugary foods), portion sizes, level of physical activity, and the presence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes. Stress, sleep quality, and hydration also play a role in regulating blood sugar following meals.