Last updated on December 30th, 2024 at 11:58 am
Stye Treatment – A hordeolum, commonly referred to as a stye, represents a prevalent and frequently uncomfortable infection affecting the eyelid. It occurs when one or more oil glands at the base of an eyelash become blocked, leading to the development of a red, tender bump. While styes are generally harmless, they can be uncomfortable and aesthetically displeasing. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various effective treatments for styes.
Styes are typically caused by a bacterial infection, commonly Staphylococcus aureus. These bacteria are naturally present on the skin and can enter the oil glands through small cuts or abrasions. Other contributing factors to stye treatment include poor eyelid hygiene, using expired or contaminated cosmetics, and frequently rubbing the eyes with dirty hands.
Symptoms of Styes
Identifying a stye early on can help in implementing effective treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and Swelling: The affected area of the eyelid becomes red and swollen.
- Pain: Styes are often tender and painful, especially when touched.
- Watering of the Eye: Excessive tearing may occur due to irritation.
- Blurred Vision: In some cases, vision may be temporarily affected.
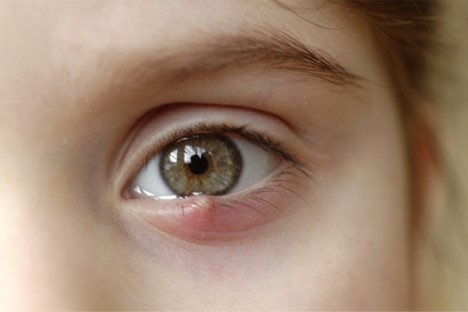
Stye Treatment
The best and most effective treatment of stye is mentioned below:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eye several times a day helps promote drainage and relieve pain. Soak a clean cloth in warm water and gently place it over the closed eye for 10-15 minutes.
- Eyelid Hygiene: Keep the affected eye clean by using a mild, fragrance-free soap or baby shampoo to cleanse the eyelids. Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly before touching the infected area.
- Avoid Squeezing: Resist the urge to squeeze or pop the stye, as this can lead to further infection or the formation of a more severe condition called a chalazion.
- Antibiotic Ointments: Over-the-counter antibiotic ointments, such as bacitracin or erythromycin, can be applied to the eyelid to help eliminate bacterial infection. It’s crucial to follow the instructions provided and consult a healthcare professional if the condition persists.
- Oral Antibiotics: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed by a doctor to combat the infection. This is usually reserved for styes that do not respond to topical treatments.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are effective in alleviating pain and mitigating inflammation.
- Contact Lens Consideration: If you wear contact lenses, temporarily switch to glasses until the stye heals. Contact lenses may exacerbate the irritation and hinder the healing process.
Also, Check:
- Eye Flu Medicine
- What is Allergy?
- Best Laser Treatment for Eyes
- Laser Treatment for Eyes in Hindi
- Which Eye Condition Deserves More Attention?
When to Seek Medical Attention for Stye Treatment
While most styes can be effectively treated at home, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if:
- The stye persists or worsens after a week of home treatment.
- Vision is significantly affected.
- The stye is recurrent or accompanied by other symptoms like fever.
> Consult a Doctor and Medkart will help you Order Medicines Online
Internal Stye Treatment
While external styes are commonly visible on the eyelid, internal styes, also known as internal hordeolums, develop inside the eyelid. These can be more challenging to identify and treat due to their location. Similar to external styes, internal styes are primarily caused by a bacterial infection, often Staphylococcus aureus.
- Avoid Eye Makeup: Refrain from using eye makeup until the internal stye has healed to prevent further irritation and contamination.
- Topical Antibiotics: Your healthcare professional may recommend topical antibiotics in the form of ointments or drops to combat the bacterial infection. Follow the prescribed instructions carefully.
- Oral Antibiotics: In more severe cases or if the internal stye does not respond to topical treatments, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to address the infection systemically.
- Incision and Drainage (if necessary): In rare cases, a healthcare professional may need to perform a minor incision to drain the internal stye if it doesn’t respond to conservative treatments.
- Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
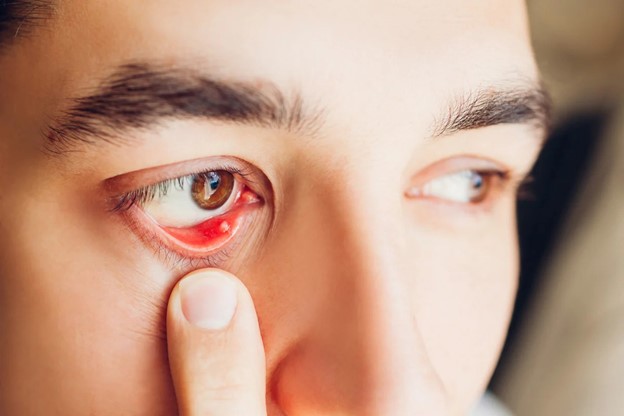
Conclusion:
Styes are common eye infections that can be managed effectively with proper hygiene and home treatments. By incorporating warm compresses, maintaining good eyelid hygiene, and using appropriate medications, individuals can relieve symptoms and facilitate the healing process. However, if the condition persists or worsens, seeking professional medical advice is crucial to prevent potential complications. Remember, early intervention and consistent care are key to a speedy recovery from styes.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
FAQs on Stye Treatment
Q1. What is Stye Treatment?
Stye treatment typically involves warm compress application to reduce inflammation, maintaining good eyelid hygiene, and using over-the-counter or prescribed antibiotics to address bacterial infection. In more severe cases, oral antibiotics or professional drainage procedures may be recommended.
Q2. Can I treat a stye at home?
Yes, home treatment includes applying warm compresses, practising good eyelid hygiene, and using over-the-counter antibiotic ointments to alleviate symptoms.
Q3. Should I pop or squeeze a stye?
No, attempting to pop or squeeze a stye can worsen the infection and lead to complications. It’s best to apply warm compresses and seek professional advice if needed.
Q4. When should I see a doctor for a stye?
Consult a doctor if the stye persists after a week of home treatment, if vision is affected, or if the stye is accompanied by fever. Professional guidance ensures appropriate intervention if required.
Related Links:
