Last updated on November 13th, 2024 at 06:23 pm
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart: Sustaining optimal blood sugar levels is essential for holistic health and well-being. Whether you are managing diabetes or simply interested in optimizing your health, understanding the nuances of blood sugar levels is essential. This blog will explore the normal blood sugar levels chart, factors influencing blood sugar, and practical tips for maintaining balance.
Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary fuel for the cells in the body, providing essential energy for their functioning. The pancreas plays a central role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose. Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, influenced by factors such as food intake, physical activity, and stress.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
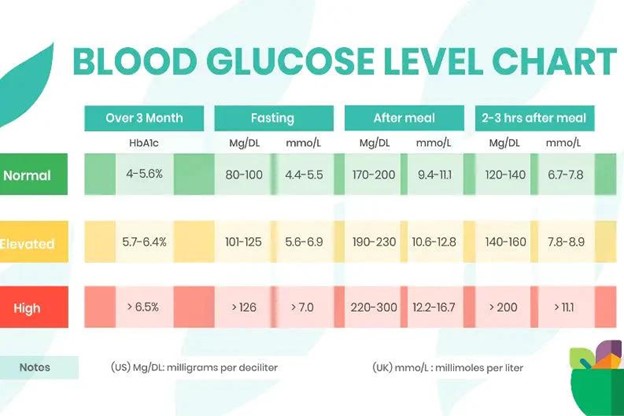
The American Diabetes Association provides a general guideline for normal blood sugar levels. It’s important to note that individual variations may occur, and consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable for personalized advice. The following values are typically considered normal and the sugar level chart is mentioned below:
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
- Normal Range: 70-99 mg/dL
- Fasting blood sugar is measured after an overnight fast, providing a baseline level.
Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) or After Meals
- Normal Range: Less than 140 mg/dL
- This measurement reflects blood sugar levels 2 hours after consuming a meal.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
- Normal Range: Less than 5.7%
- HbA1c provides a longer-term view of blood sugar control over the past 2-3 months.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can impact blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming a balanced diet with a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, promoting better blood sugar control.
- Stress: Stress hormones can elevate blood sugar levels. Implementing stress-reduction techniques is beneficial.
- Medications: Certain medications, including insulin and oral diabetes medications, can affect blood sugar levels.
Tips for Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables in your meals.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Monitor Your Levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider to track changes and make necessary adjustments.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water is essential for overall health and can help maintain blood sugar levels.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to keep stress levels in check.
Also, Read:
- How to Remove Dark Circles?
- How to Lose Weight Fast?
- How To Reduce Belly Fat
- How Many Calories in an Apple?
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart By Age
As we journey through life, our bodies undergo various changes, and one aspect that demands our attention is blood sugar levels. Understanding the normal range for different age groups is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Let’s discuss normal blood sugar levels chart by age stages of life, providing insights into the variations and significance at each age.
Infancy and Childhood
During the early stages of life, blood sugar levels in infants and children may vary from those in adults. Generally, the normal fasting blood sugar range for newborns is 30-100 mg/dL. As children grow, the levels tend to align more closely with adult ranges, reaching approximately 70-100 mg/dL.
Adolescence
The adolescent years mark a period of rapid growth and hormonal changes. Normal fasting blood sugar levels during adolescence typically fall within the range of 70-100 mg/dL, mirroring the adult standard. However, individual variations may occur, and it’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels, especially for those with a family history of diabetes.
Adulthood
In adulthood, maintaining stable blood sugar levels becomes increasingly crucial. The general normal fasting blood sugar range for adults is 70-100 mg/dL. Postprandial levels, or blood sugar levels after meals, are considered normal if they stay below 140 mg/dL. Regular monitoring becomes vital as the risk of conditions like Type 2 diabetes may increase with age.
Elderly
As individuals age, factors such as decreased insulin sensitivity and other health conditions can impact blood sugar levels. The normal fasting blood sugar range for the elderly is often considered to be 70-110 mg/dL. Regular health check-ups and monitoring become imperative to catch any deviations and address them promptly.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy introduces additional considerations, as gestational diabetes can affect blood sugar levels. Fasting blood sugar levels during pregnancy typically range from 60-95 mg/dL, with postprandial levels staying below 120 mg/dL. Close monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers are crucial for the well-being of both the mother and the developing baby.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Understanding the normal blood sugar levels by age is essential, but it’s equally important to recognize the factors that can influence these levels. Lifestyle choices, diet, physical activity, and genetics all play significant roles. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management contribute to overall blood sugar control.
Conclusion:
Understanding and maintaining normal blood sugar levels is fundamental to overall health and plays a pivotal role in preventing and managing conditions like diabetes. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar levels, and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving and sustaining optimal blood sugar control. Remember, personalized advice from healthcare providers is crucial for tailoring recommendations to individual needs.
In the intricate tapestry of life, our bodies undergo dynamic changes, and blood sugar levels reflect this journey. Understanding the normal blood sugar levels chart by age empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal health. Regular monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, and collaboration with healthcare professionals create a holistic approach to well-being across the ages. Remember, knowledge is the key to a healthier, more informed life at every stage.
Read: What are Generic Medicines?
FAQs on Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Q.1 What is the normal fasting blood sugar range, and why is it important?
Answer : The normal fasting blood sugar range is 70-99 mg/dL. This baseline measurement, taken after an overnight fast, provides crucial insights into your body’s ability to regulate glucose, a key factor in overall health.
Q.2 How do postprandial blood sugar levels differ, and what is the acceptable range after meals?
Answer : Postprandial blood sugar levels, measured two hours after eating, should ideally stay below 140 mg/dL. This range reflects the body’s ability to manage glucose levels effectively in response to food intake.
Q.3 What role does Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) play in assessing blood sugar control over time?
Answer : HbA1c provides a longer-term view of blood sugar control, covering 2-3 months. The normal range is less than 5.7%, offering valuable information for individuals managing or preventing conditions like diabetes.
Q.4 How does age impact normal blood sugar levels, and what are the general ranges across different life stages?
Answer : Blood sugar levels can vary with age. In infancy and childhood, the range is 70-100 mg/dL, aligning with adult levels as children grow. During adolescence and adulthood, fasting levels typically range from 70-100 mg/dL. For the elderly, the range may extend up to 110 mg/dL, emphasizing the importance of age-appropriate monitoring.
Related Links:
- Why Symptoms of Diabetes are Not Detected Early
- Exercise for High Blood Pressure
- Stress Management for High Blood Pressure
- Are Generics Available for Diabetes Treatment
- Are You at Risk for Diabetes
- Does smoking increase the risk of Gestational Diabetes
- What is Diabetes? – Types of diabetes, Symptoms ,Treatment
- How stress and mental health can lead to diabetes
- What Are the Reasons for Diabetes in Children and How to Manage It
- Are Generics available for Diabetes


